A PHE IEC material is posted in Sitio Sapao, Cawag, Subic, Zambales. A women-managed area was established in the partner community where women are trained as peer educators in ecosystem approach to fisheries management (EAFM) and sexual and reproductive health and rights (SRHR).
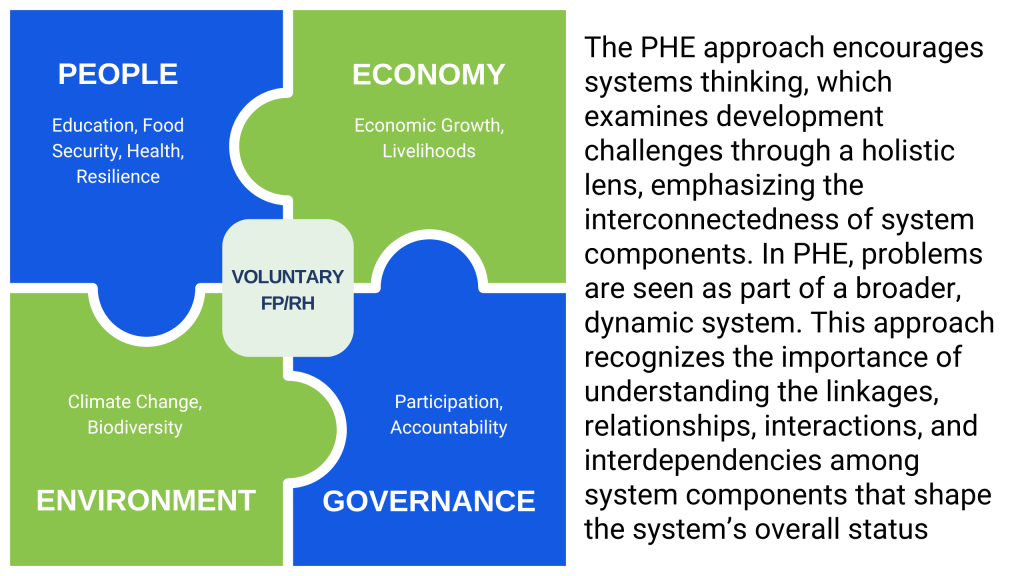
The rationale for the PHE approach stems from the understanding that population, health and the environment are inextricably linked and that dealing with these issues individually is inadequate for attaining sustainable development. Traditional approaches to development frequently focus on a single sector at a time, resulting in fragmented initiatives that may overlook the underlying causes of problems or fail to address the broader context in which these challenges emerge. The PHE approach, on the other hand, recognizes the need for integrated solutions that consider the complex interplay between population dynamics, health outcomes and environmental sustainability.
- Population Dynamics: Rapid population growth can increase the demand for natural resources, exerting stress on ecosystems and contributing to environmental degradation. In addition, high population density can put a burden on healthcare systems, making it harder to provide adequate care to all individuals. The PHE approach addresses population dynamics through family planning and reproductive health services, which helps manage population growth, minimize demand on natural resources and enhance health outcomes, especially among women and children.
- Health Outcomes: Health and well-being are deeply connected to environmental conditions. Poor environmental quality, like polluted air and water, worsened by rapid population growth, can cause various health issues, including respiratory problems, waterborne diseases and malnutrition. On the other hand, healthy ecosystems offer essential services that support human health, such as clean air, safe water, nutritious food and protection from natural disasters. When individuals and families are healthy, they are better equipped to care for their environment.
- Environmental Sustainability: Environmental sustainability is essential for ensuring the long-term well-being of communities. Unsustainable practices, such as deforestation, overfishing and pollution, can lead to the degradation of natural resources, threatening the livelihoods and health of communities. The PHE approach promotes sustainable practices that conserve natural resources alongside health interventions, thereby creating more resilient communities that are better able to adapt to changing environmental conditions.
Benefits of the PHE approach
The PHE approach offers numerous benefits that can lead to more sustainable and resilient communities. Some of the key benefits include:
- Improved Health Outcomes: By integrating health services with environmental conservation efforts, the PHE approach helps to improve access to healthcare, particularly in remote and underserved areas. This can lead to better health outcomes, such as reduced maternal and child mortality, improved nutrition and decreased incidence of waterborne diseases. Additionally, by addressing environmental factors that contribute to poor health, such as water pollution and overfishing, the PHE approach can help to prevent health problems before they arise.
- Environmental Conservation: The PHE approach promotes sustainable practices that conserve natural resources and protect ecosystems. By reducing population pressures on the environment through family planning and reproductive health services, the PHE approach helps to ensure that natural resources are used sustainably and that ecosystems are conserved for future generations. This is particularly important in areas where population growth is contributing to environmental degradation, such as coastal communities and forested areas where people also usually migrate in search of livelihoods.
- Empowerment of Women and Communities: The PHE approach recognizes the importance of empowering women and communities to take control of their own health and well-being. By providing access to family planning and reproductive health services, the PHE approach empowers women to make informed decisions about their reproductive health, leading not only to improved health outcomes but gender equality. Additionally, by involving communities in the management of natural resources and environmental conservation efforts, the PHE approach promotes community ownership and stewardship, leading to more sustainable and effective outcomes.
- Enhanced Resilience to Climate Change: Climate change poses significant challenges to communities, particularly those that are heavily dependent on natural resources. By integrating family planning and reproductive health into climate change adaptation programs, the PHE approach helps communities and ecosystems on which they depend better cope with the impacts of climate change, especially natural disasters.
- Cost-Effective Solutions: The PHE approach offers cost-effective solutions to complex development challenges by leveraging the synergies between population, health and environmental interventions. By addressing these issues together, the PHE approach can achieve greater impact with fewer resources compared to addressing each issue separately. This is particularly important in resource-constrained settings, where limited funding and capacity may make it difficult to address multiple development challenges simultaneously.

Key strategies in implementing the PHE approach
Successfully implementing the PHE approach requires coordinated efforts across multiple sectors, including health, environmental conservation and population and development. Some of the key strategies for implementing the PHE approach include:
- Integrated Service Delivery: One of the core strategies of the PHE approach is the integrated delivery of services across population, health and environment sectors. This involves providing health services, such as family planning and reproductive health, alongside environmental conservation activities, such as reforestation or sustainable agriculture. By delivering services in an integrated manner, the PHE approach ensures that communities receive comprehensive support that addresses their needs in a holistic way.
- Community Engagement and Participation: Engaging communities in the design, implementation and monitoring of PHE interventions is essential for ensuring that these interventions are effective and sustainable. Community participation helps to build ownership and trust, leading to more successful outcomes. Additionally, involving communities in decision-making processes allows for the incorporation of local knowledge and perspectives, which can enhance the relevance and suitability of PHE interventions.
- Capacity Building and Training: Building the capacity of local organizations, government agencies and community groups to implement and sustain PHE interventions is critical for long-term success. This includes providing training on integrated service delivery, community engagement and sustainable practices, as well as supporting the development of local leadership and governance structures. Capacity building also involves strengthening the ability of communities to monitor and evaluate PHE interventions, ensuring that they are able to adapt and improve over time.
- Policy Advocacy and Integration: Advocacy for the integration of PHE into national and local policies is essential for scaling up the approach and ensuring its sustainability. This involves working with policymakers and decision-makers to raise awareness of the benefits of the PHE approach and to promote its inclusion in relevant policies, plans and programs. Policy advocacy also includes efforts to secure funding and resources for PHE initiatives, as well as to create enabling environments for their implementation.
- Monitoring, Evaluation and Learning: Monitoring and evaluation (M&E) are critical components of the PHE approach, as they allow for the assessment of progress, identification of challenges and adaptation of interventions as needed. Knowledge management is also crucial alongside M&E to generate and communicate evidence that are needed to promote the approach to decision-makers.
- Strengthening the Community of Practice: Strengthening the PHE community of practice is critical because it serves as a platform for stakeholders to continuously collaborate, share knowledge and build capacity. A well-connected community of practice improves the promotion of the PHE approach across sectors by drawing on various skills and experiences, resulting in more effective and scalable interventions. A strong community of practice also serves as a venue to push for scaling up of PHE initiatives based on the most recent data and best practices. Convergence through the community of practice helps to maintain momentum and commitment to the PHE advocacy.
Read Part 1 here.





