Participants flock a booth during the PHE Youth Festival, a pre-conference activity for the 9th National PHE Conference held in October 2023 in Iloilo City.
In the face of interconnected global challenges, an integrated approach that addresses the interconnectedness of the health of people and the planet vis-à-vis population dynamics is vital. This is where the population, health and environment (PHE) approach comes into play.
PHE is a development approach that seeks to simultaneously tackle issues related to population dynamics, human and ecological health and other development issues ranging from food security to climate change adaptation. It recognizes that these elements are deeply interrelated and that addressing them together is more effective and cost-efficient and can lead to more sustainable and resilient communities
Defining the PHE approach
The PHE approach integrates interventions that address the interlinked challenges of population dynamics, human health and the state of the environment. It is based on the understanding that human health and wellbeing are inextricably linked to the health of the environment. The PHE approach advocates for coordinated efforts across these sectors—and beyond—to produce the most comprehensive and responsive development outcomes. By addressing multi-sectoral issues at once, the PHE approach aims to create synergies that lead to greater overall impact compared to addressing these issues separately.
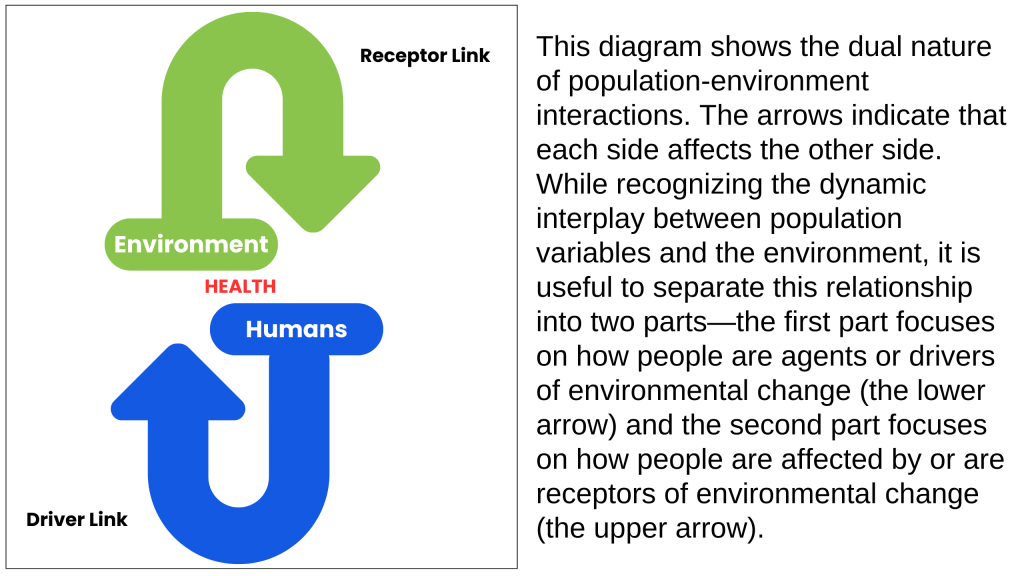
At its core, the PHE approach aims to improve the quality of life of communities by enabling them to access comprehensive healthcare services (including family planning and reproductive health) and actively participate in environmental conservation efforts. This integrated approach not only addresses the immediate needs of communities but also promotes long-term sustainability by ensuring that population growth is managed, health outcomes are improved and natural resources are conserved for future generations.
History of the PHE approach in the Philippines
The PHE approach has a rich history in the Philippines, where it has been implemented in various forms by different organizations over the past three decades. One of the earliest implementations of the PHE approach in the Philippines was through the Integrated Population and Coastal Resource Management (IPOPCORM) project, which began in the early 2000s. This project, implemented by PFPI, aimed to improve coastal resource management by addressing the population pressures that were contributing to environmental degradation. The IPOPCORM project integrated family planning services with coastal resource management initiatives.

Following the success of IPOPCORM, the PHE approach gained traction in the Philippines, with various other initiatives being launched to address the interconnected challenges faced by communities. These include projects focused on integrating reproductive health services with natural resource management, food security and access to water and sanitation while enhancing community resilience to climate change.
Over the years, the PHE approach has evolved and expanded in the Philippines, with the government, non-governmental organizations and local communities increasingly recognizing the value of integrated solutions. Today, the PHE approach is seen as a potent strategy for achieving sustainable development in the country, particularly in the face of growing challenges such as climate change and biodiversity loss.
The PHE community of practice in the Philippines has organized into a countrywide organization called PHE Network and has organized nine biennial national conferences since 2004.For more information on the history of the PHE movement in the Philippines, check this resource.
Read Part 2 here.





